CT Scan (Computed Tomography Scan)
Uses, Risks & Benefits
You are here >> Home > Blog > Cancer > Cancer Diagnosis > Diagnosis English > CT Scan
Has your doctor ever recommended a Computed Tomography (CT) Scan and you felt a little nervous or confused? You are not alone. Many people hear these medical terms and immediately start worrying. What is this machine? Is it safe? What will they find?
This guide is here to answer all your questions in simple, easy-to-understand language. We will walk you through everything, from what a CT Scan is to how much it costs in India. By the end of this article, you will feel confident and well-informed about this incredibly useful medical test. This technology is a cornerstone of modern diagnostics, providing doctors with a clear view inside your body.
Let’s demystify the CT Scan together and understand why it is such a powerful tool for your health.
- IN THIS BLOG
- CT Basics
- Types
- Recommendations
- Procedure
- Cancer
- Preparation
- Safety
- Cost
- FAQs
- IN THIS BLOG
- CT Basics
- Types
- Recommendations
- Procedure
- Cancer
- Preparation
- Safety
- Cost
- FAQs
Summary
- How CT Scans Work
- Why Doctors Recommend It
- What to Expect During the Scan
What Is a CT Scan?
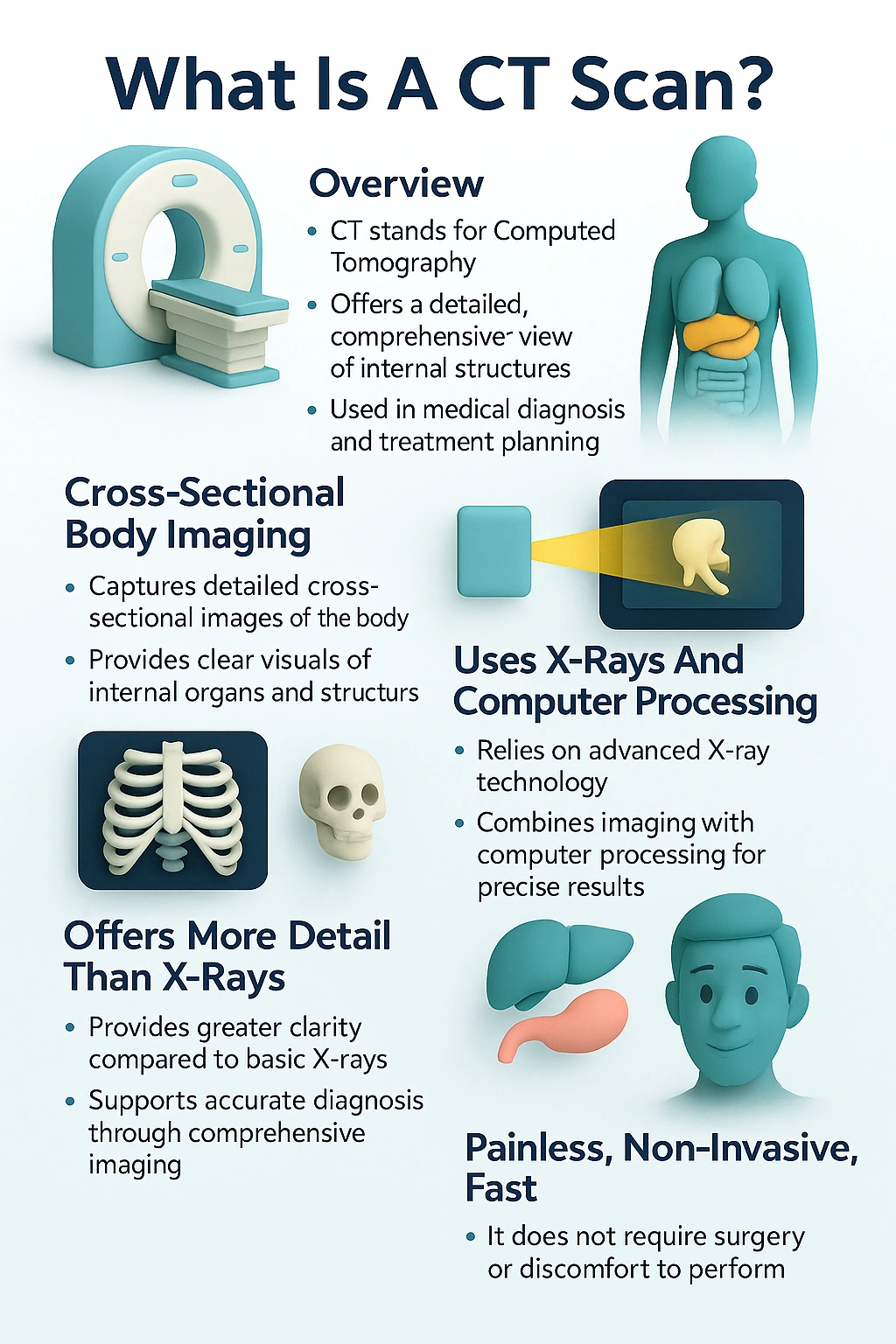
- History
- Full Form and Definition of CT Scan
- How CT Scan Works – Basic Concept
- Differences Between CT Scan and MRI
- Here is a simple table to help you understand the key differences
| Feature | Computed Tomography (CT) Scan | Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) |
|---|---|---|
| How It Works | Uses multiple X-rays to create cross-sectional images. | Uses strong magnets and radio waves to create detailed images. |
| Best For | Excellent for imaging bones, detecting cancers, chest and lung issues, and emergency situations (like after an accident) because it's very fast. | Superior for examining soft tissues like the brain, spinal cord, ligaments, and muscles. |
| Speed | Very fast; the scan itself often takes less than a minute. | Slower; can take 30 to 60 minutes or more. |
| Radiation | Involves a small, controlled dose of ionizing radiation. | No radiation is used. |
| Noise Level | Makes a whirring or humming sound. | Very loud; patients are often given earplugs or headphones. |
Types of CT Scans
- Head and Brain CT Scan
Head and Brain CT Scan: This scan is used to look at the brain and skull. It’s often done after a head injury to check for bleeding or fractures. It can also detect brain tumors, blood clots, or strokes. The computed tomography ct or cat scan of the brain is a critical tool in neurology. The ct computed tomography scan psychology definition relates to its ability to identify structural brain abnormalities that may be linked to certain psychological or neurological conditions.
- Chest and Lung CT Scan
- Abdominal and Pelvic CT Scan
- Spine and Bone CT Scan
- Cardiac (Heart) CT Scan
- CT Angiography (with Contrast)
When Is a CT Scan Recommended?
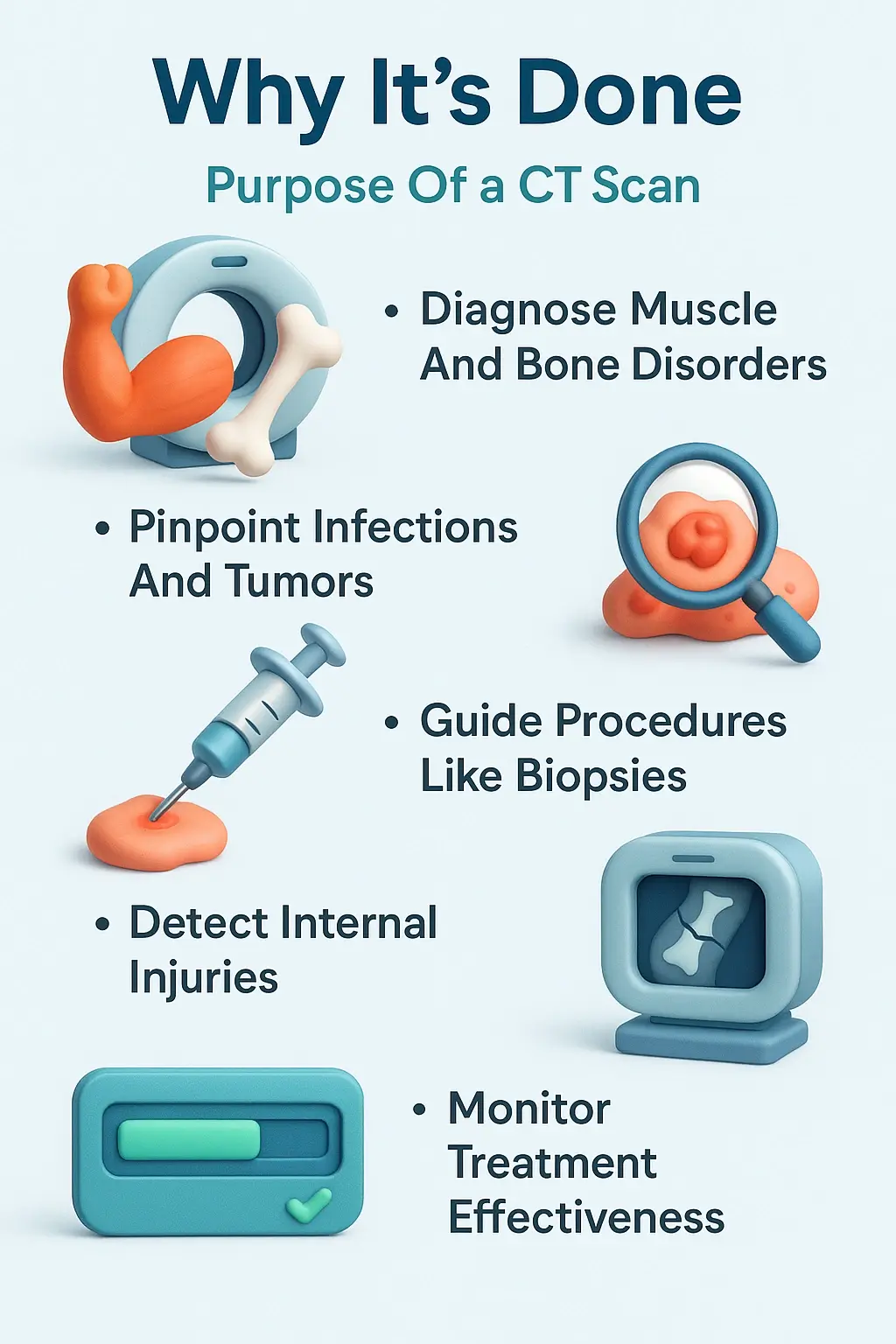
- After Injuries or Accidents
- To Detect Tumors and Cancers
One of the most important uses of a CT scan is in oncology (the study of cancer). A CT Scan can help doctors:
⦿ Find a tumor and determine its exact size and location.
⦿ See if the cancer has spread to other parts of the body.
⦿ Guide a biopsy (where a small tissue sample is taken).
⦿ Monitor if a cancer treatment is working.
This is what are ct scans used to find in many cancer-related cases.
- For Chronic Pain or Internal Infections
- Pre-Surgery Planning and Evaluations
CT Scan Procedure: What to Expect

- Step-by-Step Test Process
⦿ Check-in: You will arrive at the hospital or diagnostic center and register. You may be asked to fill out a consent form.
⦿ Preparation: A technician (radiographer) will explain the procedure. You may need to change into a hospital gown and remove any metal objects like jewelry, glasses, or dentures, as they can interfere with the images.
⦿ Positioning: You will be asked to lie down on a narrow, motorized table. The technician will help you get into the correct position. They may use pillows or straps to help you stay still and comfortable.
⦿ The Scan: The table will slowly slide into the center of the large, donut-shaped CT scanner. The scanner will begin to rotate around you, making whirring sounds. You will be alone in the room, but the technician can see, hear, and speak to you through an intercom at all times.
⦿ Holding Your Breath: For scans of the chest or abdomen, you may be asked to hold your breath for a few seconds at a time. This prevents motion and ensures the images are clear.
⦿ Finishing Up: Once the scan is complete, the table will slide out of the scanner. The technician will help you up, and you can change back into your clothes.
- Duration of the Scan
- What to Wear and How to Prepare
- Preparation Checklist for Your CT Scan
| Preparation Step | Details |
|---|---|
| Follow Fasting Instructions | If you are having a scan with contrast, food or drink can interfere with the results or cause nausea. Follow instructions precisely. |
| Remove All Metal | Metal objects (jewelry, hairpins, zippers, glasses) can create artifacts (white streaks) on the CT images, making them difficult to read. |
| Inform Doctor of Allergies | If you have any known allergies, especially to iodine or shellfish, you must tell your doctor, as this relates to the contrast dye. |
| List Your Medications | Provide a full list of your current medications to your doctor and the technician, especially if you have diabetes or kidney problems. |
| Arrange for a Drive Home (If Sedated) | In rare cases, if you are very anxious, you might be given a mild sedative. If so, you will not be able to drive yourself home. |
Role of Advanced Imaging in Cancer Detection
- How Advanced Imaging Helps Identify Tumors and Metastasis
Furthermore, this imaging is crucial for detecting metastasis, which means the cancer has spread from where it started to other parts of the body. For example, a scan of the chest, abdomen, and pelvis can check if a cancer that started in the lung has spread to the liver or bones.
- Use in Staging and Treatment Planning
This information is vital for creating the best treatment plan. Based on the scan results, doctors can decide whether surgery, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, or a combination of treatments will be most effective. A precise scan allows for more targeted and successful treatment.
- Image-Guided Biopsy and Interventional Procedures
- Monitoring Treatment Response and Recurrence
CT Scan with Contrast: What You Need to Know
- What is Contrast Dye?
Contrast dye, also known as contrast material or contrast agent, is a special liquid that helps certain organs, blood vessels, or tissues stand out more clearly on the CT images. It is usually iodine-based. Depending on the type of scan, the contrast can be given in three ways:
⦿ Intravenously (IV): Injected into a vein in your arm.
⦿ Orally: Swallowed as a drink.
⦿ By Enema: Administered through the rectum.
- When Contrast is Used
A Computed Tomography (CT) Scan with contrast is used when the doctor needs to highlight specific areas. It is particularly useful for:
⦿ Visualizing Blood Vessels: It makes arteries and veins light up, helping to find blockages, aneurysms, or other vascular problems.
⦿ Identifying Tumors: Many tumors have a different blood supply than normal tissue, and the contrast dye makes them easier to see.
⦿ Checking for Inflammation or Infection: Areas of inflammation or infection often show up more clearly after contrast is administered.
- Risks and Allergic Reactions
However, there are small risks. Some people may have a mild allergic reaction, like itching or a rash. Severe allergic reactions are very rare but can happen. It is crucial to tell your doctor if you have ever had a reaction to contrast dye before, or if you have allergies to iodine or shellfish. Also, inform them if you have kidney problems, as the kidneys are responsible for filtering the dye out of your body.
How to Prepare for a CT Scan

- Fasting or Hydration Instructions
- Informing Your Doctor About Medical History
It is very important that your doctor knows your complete medical history before you have a computed tomography CT scan. Be sure to tell them about:
⦿ Any allergies you have.
⦿ Any kidney disease or diabetes.
⦿ Any heart conditions.
⦿ If you are pregnant or think you might be pregnant.
⦿ Any medications you are currently taking.
- Pre-scan Checklist and Consent
Interpreting CT Scan Results
- How Results Are Generated and Shared
- When to Expect the Report
- What to do After Getting Abnormal Results
- Common Conditions Diagnosed by Different CT Scan Types
| Type of CT Scan | Common Conditions It Helps Diagnose |
|---|---|
| Head & Brain | Stroke, brain tumors, bleeding after injury, skull fractures, blood clots. |
| Chest & Lung | Pneumonia, lung cancer, pulmonary embolism (blood clot in lungs), tuberculosis, chest injuries. |
| Abdomen & Pelvis | Appendicitis, kidney stones, liver disease, pancreatitis, intestinal blockages, abdominal cancers. |
| Spine & Bone | Herniated discs (slipped disc), spinal fractures, bone tumors, spinal stenosis (narrowing of the spinal canal). |
| Cardiac (Heart) | Coronary artery disease (calcium scoring), aortic aneurysms, problems with heart structure. |
| CT Angiography | Blockages or narrowing of arteries, aneurysms (bulges) in the aorta or brain vessels. |
CT Scan Risks & Safety

- Radiation Exposure – Is It Harmful?
- Safety in Children and Pregnant Women
- When to Avoid CT Scans
Cost of CT Scan in India
- Price Based on Body Part and City
- Government vs Private Scan Centers
Conclusion
While the thought of any medical test can be a bit daunting, we hope this detailed guide has made you feel more comfortable and informed about the procedure. Remember, a Computed Tomography (CT) Scan is a safe and powerful tool used to protect your most valuable asset: your health. Always feel free to ask your doctor or the radiology technician any questions you may have. Your peace of mind is an important part of your healthcare journey.
Frequently asked questions

Dr. Harsh Shah
MS, MCh (GI cancer Surgeon)
Dr Harsh Shah is a well known GI & HPB Robotic Cancer Surgeon in Ahmedabad. He treats cancers of Esophagus, stomach, liver, pancreas, colon, rectum & small intestines. He is available at Apollo Hospital.

